Examples¶
Example 1: A simple network of coupled Montbrio model nodes.
Starting with a few imports
import os
import vbjax as vb
import jax.numpy as np
os.makedirs('images', exist_ok=True)
This example shows how to use the vbjax library to simulate a network of
Montbrio model nodes. The network is defined by the function network which
takes as arguments the state of the network and the parameters of the model.
The function returns the time derivative of the state of the network.
def network(x, p):
c = 0.03*x.sum(axis=1)
return vb.mpr_dfun(x, c, p)
The function make_sde is used to create a function loop that simulates the
network for a given time interval and a given set of initial conditions.
_, loop = vb.make_sde(dt=0.01, dfun=network, gfun=0.1)
The function vb.randn is used to generate a set of noise samples.
The dimesions are (time, state, node). The first noise sample is used as the
initial condition of the network. The remaining noise samples are used to
generate the noise term of the stochastic differential equation.
zs = vb.randn(500, 2, 32)
The function loop takes as arguments the initial conditions of the network,
vector of noise samples, and the parameters of the model. The function returns
the state of the network at each time step.
xs = loop(zs[0], zs[1:], vb.mpr_default_theta)
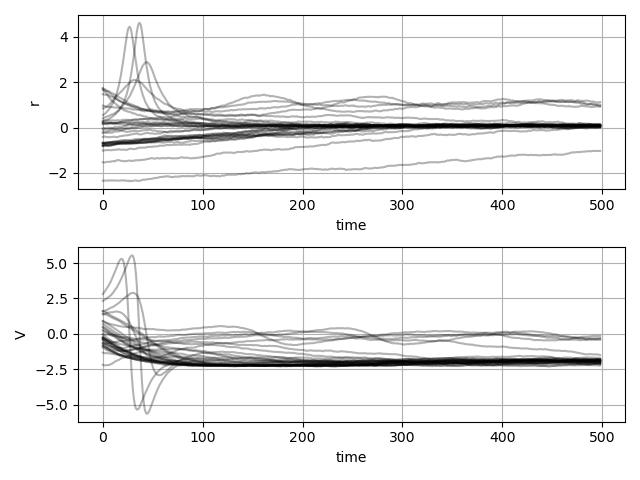
The function vb.plot_states is used to plot the state of the network. The
function takes as arguments the state of the network, the format of the plot,
and the name of the output file.
vb.plot_states(xs, 'rV', jpg='images/example1', show=False)
Example 2: Consider a network of coupled Montbrio model nodes and sweep over the parameters of the model.
Starting with a few imports
import os
import time
import vbjax as vb
import pylab as pl
import jax, jax.numpy as np
os.makedirs('images', exist_ok=True)
This example shows how to use the vbjax library to simulate a network of
Montbrio model nodes. The network is defined by the function network which
takes as arguments the state of the network and the parameters of the model.
def network(x, p):
r, v = x
k, _, mpr_p = p
c = k*r.sum(), k*v.sum()
return vb.mpr_dfun(x, c, mpr_p)
The function noise is used to generate the noise term of the stochastic
def noise(_, p):
_, sigma, _ = p
return sigma
The function run is used to simulate the network for a given set of parameters.
def run(pars, mpr_p=vb.mpr_default_theta):
k, sig, eta = pars # explored pars
p = k, sig, mpr_p._replace(eta=eta) # set mpr
xs = loop(rv0, zs, p) # run sim
std = xs[400:, 0].std() # eval metric
return std # done
Then prepare the simulation
n_nodes = 8
define the number of nodes in the network.
using_cpu = jax.local_devices()[0].platform == 'cpu'
if using_cpu:
run_batches = jax.pmap(jax.vmap(run, in_axes=1), in_axes=0)
else:
run_batches = jax.vmap(run, in_axes=1)
defines the engine to be used for the simulation. If the simulation is run on
the CPU, then the simulation is parallelized over the cores of the CPU using jax.pmap.
Otherwise, the simulation is parallelized over the GPU using jax.vmap.
then we prepare the network and the noise samples
# prepare network
_, loop = vb.make_sde(0.01, network, noise)
rv0 = vb.randn(2, n_nodes)
The rest run the simulation on set of parameters and plot the results.
# sweep sigma but just a few values are enough
sigmas = [0.0, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4]
results = []
ng = vb.cores*4 if using_cpu else 32
for i, sig_i in enumerate(sigmas):
# create grid of k (on logarithmic scale) and eta
log_ks, etas = np.mgrid[-9.0:-2.0:1j*ng, -4.0:-6.0:1j*ng]
# reshape grid to big batch of values
pars = np.c_[
np.exp(log_ks.ravel()),
np.ones(log_ks.size)*sig_i,
etas.ravel()].T.copy()
# cpu w/ pmap expects a chunk for each core
if using_cpu:
pars = pars.reshape((3, vb.cores, -1)).transpose((1, 0, 2))
# now run
result = run_batches(pars).block_until_ready()
results.append(result)
toc = time.time()
print(f'elapsed time for sweep {toc - tic:0.1f} s')
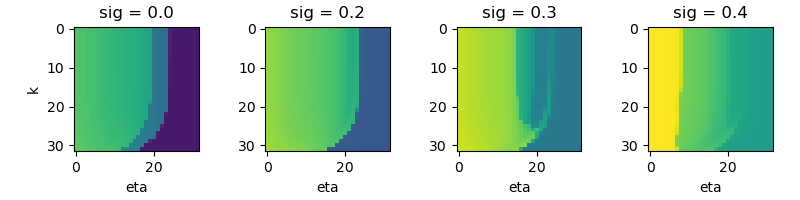
pl.figure(figsize=(8, 2))
pl.figure(figsize=(8,2))
for i, (sig_i, result) in enumerate(zip(sigmas, results)):
pl.subplot(1, 4, i + 1)
pl.imshow(result.reshape(log_ks.shape), vmin=0.2, vmax=0.7)